

The concept of heat transfer coefficient is also used in heat transfer with phase transformations in liquid (boiling, condensation). When the heat capacity of the fluid varies substantially, the heat transfer coefficient is frequently determined in terms of enthalpy difference (h w – h f).
#Heat flux equation free
In the case of free convection, the Nu number depends on the Gr and Pr numbers. In the case of fully developed heat transfer in a circular tube with laminar fluid flow the Nusselt number is a constant, namely Nu = 3.66 at a constant wall temperature and 4.36 at a constant heat flux (see Tubes (single-phase heat transfer in)).
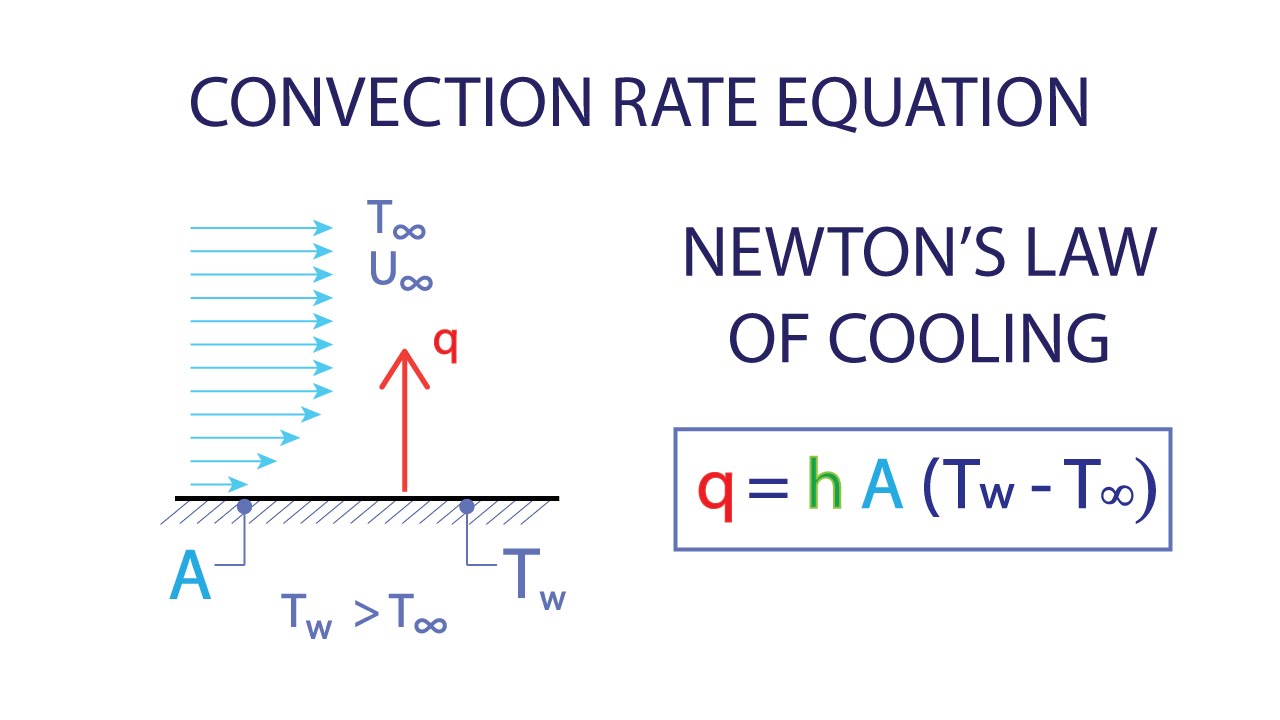
The dependence of the Nu and St numbers on the Re and Pr numbers plays an essential role in heat transfer by forced convection. Here, it is useful to use a dimensionless independent parameter, the Biot number Bi = αl/λ s, where λ s is the thermal conductivity of a solid and 1 its characteristic dimension. When solving the problems of heat conduction in a solid, the distribution of heat transfer coefficient α between the body and its surroundings is often given as a boundary condition. The Nusselt number Nu = αl/λf or the Stanton number St = is used as a dimensionless number for heat transfer in these equations, where 1 is the characteristic dimension of the surface in the flow, the mass velocity of the fluid flow, λ f and C pf the fluid thermal conductivity and heat capacity. These relations are said to be generalized or similarity equations (formulas). Using the methods of similarity theory, the dependence of heat transfer coefficient on many factors can be represented in many cases of practical importance as compact relations between dimensionless parameters, known as similarity criteria. Heat transfer coefficient depends on both the thermal properties of a medium, the hydrodynamic characteristics of its flow, and the hydrodynamic and thermal boundary conditions. The heat transfer coefficient has gained currency in calculations of convective heat transfer and in solving problems of external heat exchange between a heat conducting solid medium and its surroundings. The unit of measurement in the international system of units (SI) (see International system of units) is W/(m 2K), 1 W/(m 2K) = 0.86 kcal/(m 2h☌) = 0.1761 Btu/(hft 2☏) or 1 kcal/(m 2h☌) = 1.1630 W/(m 2K), 1 Btu/(hft 2☏) = 5.6785 W/(m 2K). Where is the heat flux density on the wall, T w the wall temperature, T t the characteristic fluid temperature, e.g., the temperature T e far from the wall in an external flow, the bulk flow temperature T b in tubes, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
